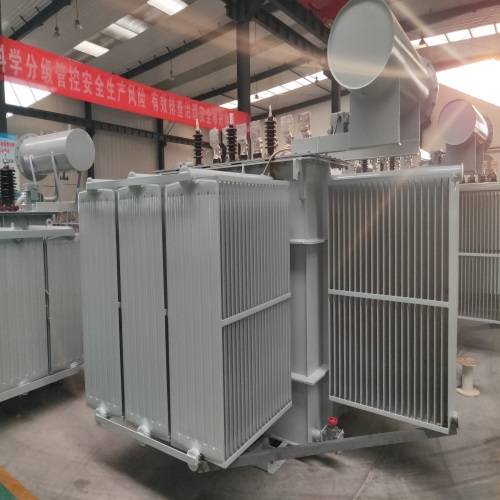
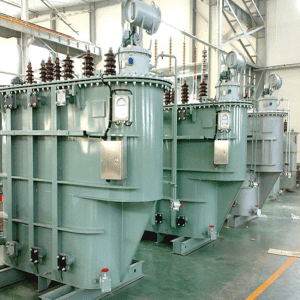
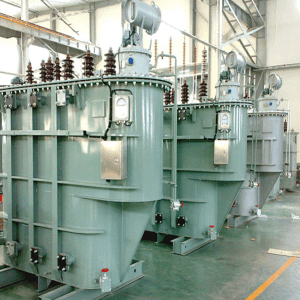
Product description
As an important power equipment, the design of the structure size of the oil-immersed transformer is not only related to the performance of the transformer, but also directly affects its installation and use in the power system. Below, we will introduce and analyze the structural dimensions of oil-immersed transformers in detail.
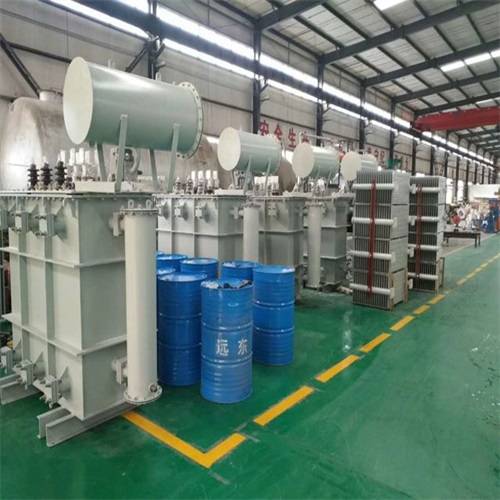
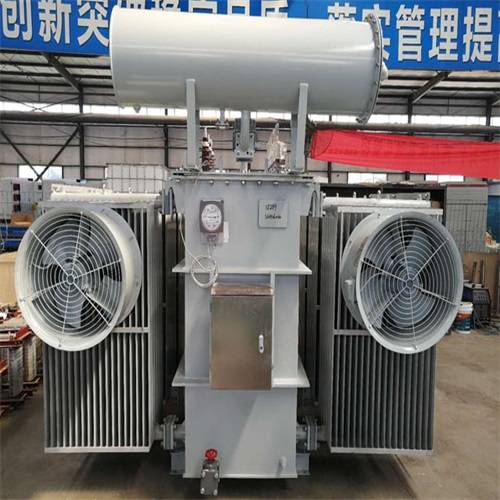
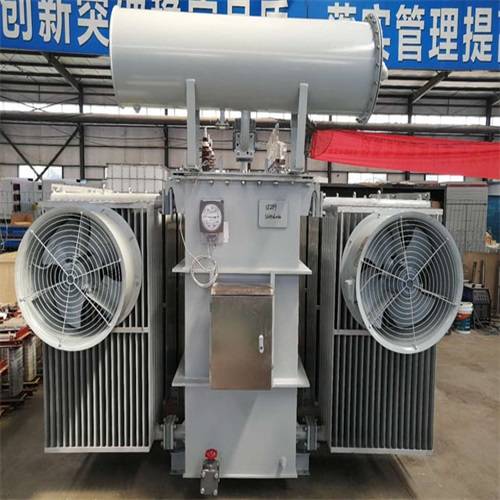



First of all, the oil-immersed transformer is mainly composed of iron core, winding, oil tank, cooling device, voltage regulating device, protection device and other parts. The core and windings are the core components of the transformer, and they realize the transformation of voltage and current through the principle of electromagnetic mutual induction. The oil tank is used to hold transformer oil, which plays the role of insulation and heat dissipation. The cooling device, voltage regulating device and protection device are responsible for the cooling, voltage regulation and safety protection of the transformer, respectively.
In terms of structural dimensions, the size of an oil-immersed transformer is usually determined according to factors such as its capacity, voltage level and use environment. Generally speaking, the larger the capacity and the higher the voltage level, the larger the structure size. This is because high-capacity transformers require more core and winding materials, as well as larger fuel tanks to hold transformer oil and dissipate heat.
Specifically, the external dimensions of oil-immersed transformers usually include three directions: length, width, and height. The length and width are mainly determined by the size of the core and windings, while the height is affected by the tank, cooling unit and other accessories. For example, an oil-immersed transformer with a capacity of 1000kVA may be about 2 meters long, 1.5 meters wide and 2.2 meters high, respectively. Of course, this is only an approximate value, and the specific size needs to be determined according to the specific design and manufacturing requirements of the transformer.
In addition, the structural dimensions of oil-immersed transformers are also affected by some special factors. For example, in order to enhance the heat dissipation performance of the transformer, the oil tank is usually designed with a corrugated sheet structure, which not only has a breathing function to compensate for the change in the volume of the oil caused by temperature changes, but also isolates the transformer oil from the outside world to prevent the entry of oxygen and moisture from leading to the decline of insulation performance. While this design increases the complexity of the tank, it also significantly improves the performance and reliability of the transformer.
At the same time, in order to meet the needs of different environments and installation conditions, the structural dimensions of oil-immersed transformers will also change. For example, in some space-constrained locations, a compact transformer design may be required to reduce its footprint. In some occasions that need to withstand large mechanical stress, it is necessary to strengthen the structural strength of the transformer to ensure its safe and stable operation.
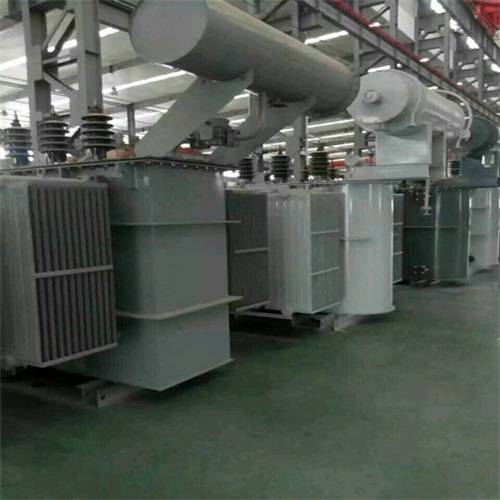
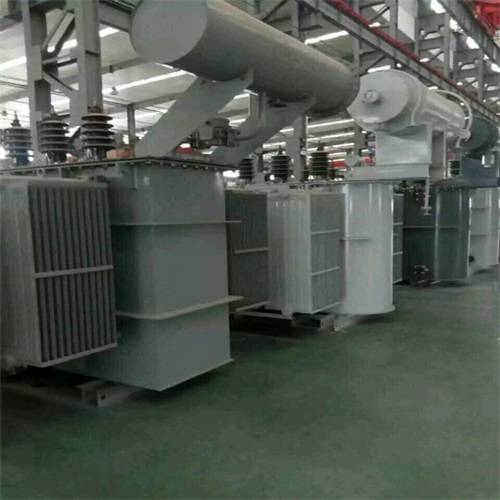


In general, the structural size of oil-immersed transformer is a complex and changeable problem, which involves many aspects such as the design, manufacture, installation and use of transformer. Therefore, when selecting and using oil-immersed transformers, it is necessary to consider the actual situation comprehensively to ensure that they can meet the needs of the power system and give full play to the best performance.
For more information on the dimensions of oil-immersed transformers, it is recommended to consult the relevant technical manuals, professional books or consult a professional electrical engineer. These resources provide more in-depth and specific guidance and assistance to better understand and apply oil-immersed transformers.